A case of acute limb ischemia due to arterial thrombus formation following trauma
A 60 year old male patient presented with history of trauma and injury in the posterior aspect of left thigh 6 days back. He developed swelling in this region. Patient also had pain, loss of sensation, absent distal pulse. A clinical diagnosis of compartment syndrome was made.
 |
| Volume rendering reconstruction of CT angiography demonstrates occlusion of the distal left superficial femoral artery with multiple collateral formation maintaining the distal flow. |
 |
| CT axial sections at the level of thigh demonstrates multiloculated collection in the medial aspect of left thigh in the inter muscular plane. |
From clinical and radiological evaluation a diagnosis of acute limb ischemia due to thrombus formation following trauma is made.
Acute limb ischemia
Acute limb ischemia occur when a leg or foot suffers from inadequate blood flow to maintain vital metabolic functions. Both arterial embolism and arterial thrombosis precipitate acute limb ischemia. By convention patient will be presenting with symptoms less than 2 weeks.
It can be due to embolism or thrombosis.
Thrombosis can be due to plaque progression and complication, thrombosis of popliteal artery aneurysm, trauma or graft thrombosis.
Embolism can be due to cardiac embolization, aortic embolization, thrombosed graft, ergotism, hypercoagulable state, paradoxical venous to arterial embolization, iatrogenic complications related to endovascular procedures.
Clinical features : pain, pallor, parasthesia, pulse deficit and poikilothermia.
The gradual progression of atherosclerosis is frequently accompanied by growth of collateral vessels to distal regions. Acute occlusion in a preconditioned limb may not produce overt ischemia. However propagation of thrombus may induce extensive ischemia.
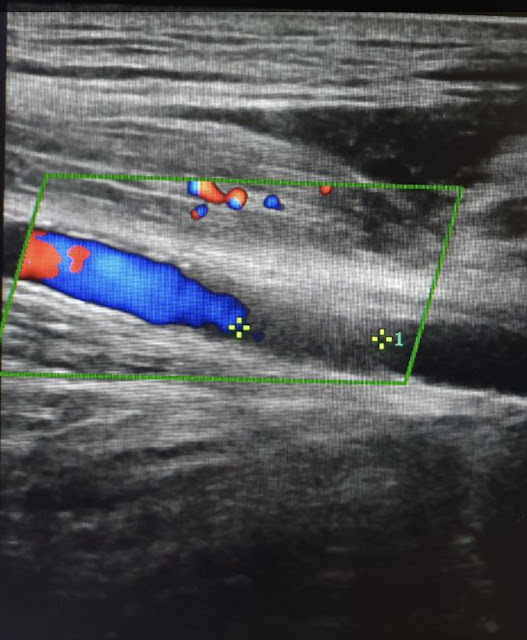
Duplex ultrasound: a pre occlusive flow has attenuated systolic peak and absent diastolic flow. Distal to an occluded segment flow is typically absent. At the site of arterial occlusion a non pulsatile artery without colour flow with a thrombus within the lumen is noted. A well delineated round thrombus in the lumen of artery without significant atherosclerotic burden will be an embolism thrombus.
Other investigations : CT angiography, Gd enhanced mr angiography, DSA





👍
ReplyDelete☺️👍
ReplyDelete